Risk Management For Ground Engineering Works.

The engineering community has successfully completed many exceptionally challenging construction projects. Unfortunately, history has shown that on occasion political, time and monetary pressures have exceeded those of the water and ground, sometimes leading to failure. Authorities have attempted to mitigate these risks through the implementation of a variety of independent design checkers and verifiers and through the provision of supervisory teams on site. These organizational systems have resulted in improvements but a common complaint is that the monitoring information is received too late and in forms which are not readily analysed or checked by the engineers. For the first time a role has been provided for an independent professional body to check, audit and deliver project monitoring data to the project stakeholders. This is in its second year on the Express Rail Link (XRL) in Hong Kong and the paper will report on its method of implementation, benefits to the project and provide guidance for those considering the management of project risk on future projects.
1. Introduction
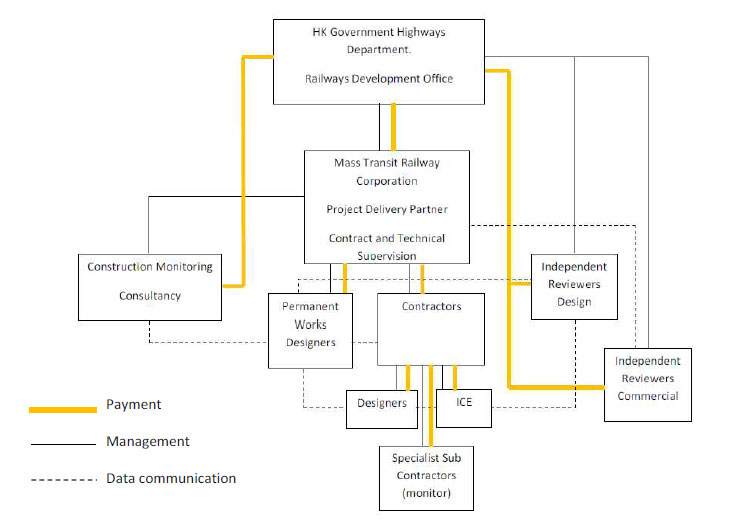
The Mass Transit Railway Corporation (MTRC) have developed the concept of the Independent Monitoring Consultancy as part of a project wide risk management initiative. This paper describes the origins of the role, its original concept and the way in which the role has evolved to become a key part of the MTRC systems. The key elements of construction monitoring can be divided into:
- Design and Prediction
- Installation of monitoring equipment
- Monitoring and communication of effects and causes
- Comparison with prediction
- Change of design or work procedures to change the rate of movement
2. Management Structure
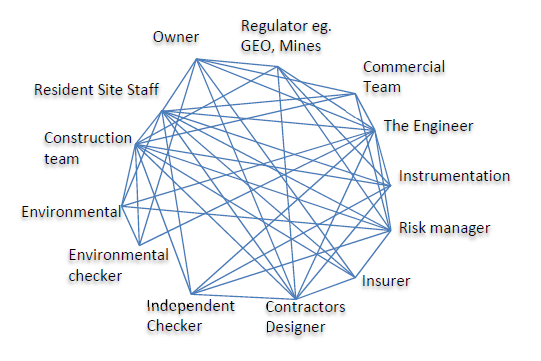
In all construction cases design and prediction is provided by the design engineer with review from the owner and associated regulatory bodies. The designer will design instrumentation to suit the monitoring of these parameters and to enable sufficient data to be collected to feedback information of the performance of the design. This is then passed to the site teams for implementation. At this time a variety of bodies become involved in the project delivery process. These are indicated in Figure 1.
The communications and interactions between these various bodies are complex but at this stage the construction is live and decisions will need to be made within a tight time framework. The ability of the management to react to change will be governed by the systems in place.
2.1 Management Challenges
With such a complex interaction, management of projects face several challenges. Much effort is put into ensuring that the objectives of all the team members are aligned towards common safety, technical and commercial goals by the use of partnering and in some cases alliancing. Historically little focus has been placed on the management of information flow between the various parties to the project.
Ultimately deviations from the prediction for the works lead to technical and commercial conflict and parties often justify their positions by “cherry picking” information to suit a particular argument. Neither party has all the information. In some cases two sets of records exist and this is counter-productive.
In fact many of the issues boil down to information.
- Handling the flow of information.
- Handling the quantity of information
- Uncertainty as to the reliability of the information received: especially if it is being recorded by separate parties who may have very specific agendas.
- Independence of the party undertaking the work
- Checking the information
- Duplication of information
- Ability to interpret the information quickly
2.2 Improvements to Management Systems
Change is a natural part of construction and the management of change should be embraced within the project management scheme. Since this is an expected occurrence the management structure should be geared to respond proactively rather than defensively. The objective should be to maximise the amount of time spent engineering rather than operating a computer.
Better information sharing and communication is required and the delivery of “agreed” factual information should be speeded up. There needs to be better cross pollination with information from other teams and facilitation of back analysis and comparison against design. Risk management should be integrated into the systems rather than being separated. Better communication, agreeing, sharing and condensing of data leads to smaller more effective teams. Efficiencies relieve time and monetary pressure which impact on quality.
2.3 Independent Monitoring versus Contractor Monitoring
In Hong Kong all construction instrumentation is carried out by the Contractor using specialist subcontractors. An estimate of 1% of construction cost is normally set aside in budgets for instrumentation of ground engineering projects within the urban environment. This should be considered as a “lower bound” and in some very complex high risk projects up to 5% has been set aside.
Monitoring within Asia tends to be seen as an imposition by the owner/designer on the Contractor to safeguard against failure or damage to the environment. Such a policing approach has not engendered buy in from Contractors and as such many will opt for the cheapest solution. If results are inconclusive or instruments fail this is seen as removing restrictions from the Contractor’s working environment. A change in attitude to one where the monitoring is considered a help would require that the contractor take some benefit from the monitoring particularly if it were to show that movements are better than predicted. Such observational engineering requires careful application but if applied would give incentive to produce quality reliable information.
In Hong Kong instrumentation Contractors are normally subcontractors of the main contractor. If time or monetary pressure is felt by the main Contractor this is normally passed on to the Instrumentation Contractor. This is particularly risky if the Contractor’s instrumentation subcontractor is also constructing temporary works. The MTRC have addressed such a conflict by requiring the instrumentation contractor to be independent of the geotechnical works.
In Singapore, all instrumentation for Government works are contracted directly to the owner. This removes any potential pressure the Contractor may bring to bear but also removes any direct involvement of the instrumentation contractor in the construction process thereby breaking the feedback loop.
3. The Independent Monitoring Consultant
3.1 Origins of the IMC role
When the KCRC and the MTRC merged in 2009 all rail ownership and rail project delivery was brought under one roof. Since this was a part public company a certain level of review was required for Government projects to be sub vented to the MTRC for development. Independent monitoring of environmental compliance has been there for some time but additional areas covering technical monitoring, finance and design were added.
Initially the independent monitoring of the West Island Line was issued as a works contract given the high proportion of measurement over consultancy services. The second independent monitoring contract was for the Regional Express Line and by this time it was issued as a Consultancy reflecting the increased focus on engineering services. The consultancy comprised:
- Physical monitoring of up to 17% of the contractor’s monitoring.
- Provision of a Unified Web database for the presentation of all monitoring
- Review of all monitoring designs
- Review of on-going monitoring and production of weekly and monthly reports.
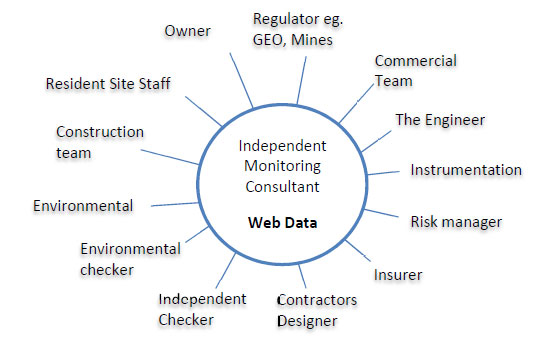
3.2 Independent physical monitoring
Low prices put pressure on quality. In some cases where resources are just not available data may be extrapolated or fudged. Often there is a focus on providing good looking graphs rather than truly representing the data. The advent of independent physical monitoring helps to ensure that the instrumentation and survey personnel provide the required frequency of measurement and that the measurements are undertaken with the required levels of accuracy.
3.3 Provision of a Unified System for
Management of Data and Independent Data Processing
The provision of a central unified system for the publishing of data to all the project members is the foundation of a new method of construction risk management. Provided by an independent third party, this system acts as the published repository for construction data which is accessible over the web to all. Secure layers are set such that on multi-contract projects parties can only see information relevant to their contract and to the contracts adjacent.
The setup of the system is designed to ensure the maximum independence of the data and speed of processing. Key aspects are:
- All data is received as raw data
- Data can be received in a number of structured formats such that the production of data for the system should require no additional steps for the suppliers
- The data can be provided from different teams within a contract such that survey can provide survey and geotechnical can provide geotechnical data. Data should not be delayed for the purpose of combining a submission.
- The data is independently processed.
- Real time data is provided to the system in real time.
- Data shall be available to the public within 30 minutes of loading
- The system shall allow unusual data to be quarantined for investigation if required but quarantined data shall be visible on the web site if it would cause an alarm.
- A GIS shows the location of the instruments and their current alarm state
- Individual items of construction work are identified and their progress is shown on the GIS
- The system is able to identify IMC data from Contractors data and easily plot this data together for comparison
- The system is able to plot large data volumes efficiently (at least 10000 records in 10 seconds)
- The system also allows progress information to be added to construction elements so that the actions which may be causing adjacent instrumentation responses can be identified and interrogated.
- AGS data or, if unavailable, PDF logs of boreholes are also added to the system to enable the geotechnical significance of movements to be determined.
- Alarms are sent by SMS and Email but also registered to the online system as part of a weblog. First response to the alarm is to the weblog and comprises a confirmation that the alarm is correct and observations as work going on in the area.
- Alarm reports are generated from the system as required by any user with those access rights.
These capabilities significantly extend those required by the original MTRC specification. This highlights the difficulties common with specifying a system implementation. Unless there is in depth knowledge of what can be done the Engineer tasked with specifying a capability has no knowledge of how difficult or much time this will take to implement, particularly when dealing with a general software house. In this case the supplier reacted to the intentions of the MTRC and provided them with achievable solutions.
Whilst the public portal is most users interface to the data this is only the tip of the iceberg. Behind the scenes systems are designed to cope with imperfect and incomplete data so that data can be presented in a timely fashion. Such systems include:



